Timeline of SUNY Downstate College of Medicine
1850's
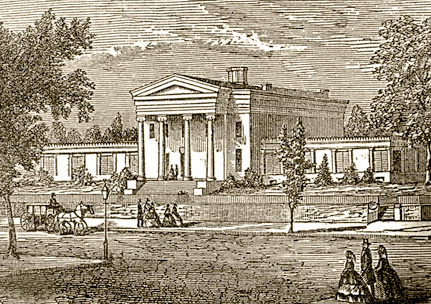 1858: The Long Island College Hospital (LICH) is founded. The Perry Mansion, located on
Henry Street between Amity and Pacific Streets in Brooklyn, serves as the first hospital
building.
1858: The Long Island College Hospital (LICH) is founded. The Perry Mansion, located on
Henry Street between Amity and Pacific Streets in Brooklyn, serves as the first hospital
building.
1859: Dr. William Dudley, Dr. Louis Bauer, and Dr. John Byrne submit formal plans for organizing a medical college and Dr. Dudley guarantees expenses. Nationwide search for medical faculty begins.
1860's
1860: Instruction of medical students in the Collegiate Division begins on March 29, 1860.
1861: Course on Military Surgery added to the curriculum as the Civil War becomes imminent and medical schools prepare to meet the needs of the nation.
1863: Frank Hastings Hamilton, MD, first Chair of Military Medicine in the United States, established after LICH begins its service as a Civil War medical base.
1864: One of the college’s most prominent alumni was Dr. Alexander J.C. Skene. Born in Aberdeenshire, Scotland, in 1838, he came to America at the age of 19 and graduated from the Long Island College Hospital in 1863. After serving in the Civil War, he entered private practice in Brooklyn in 1864. Within a year, he had begun his college and hospital work in obstetrics at the Long Island College Hospital.
He was named professor of diseases of women and clinical obstetrics in 1870, devoting the remaining 31 years of his life to the college hospital as teacher, physician, dean of the faculty from 1886 to 1892, and president of the college from 1893 to 1899.
1869: First addition to the Perry Mansion, a wing on the Pacific Street side of the facility, opened. Major change introduced in teaching curriculum as daily examinations are introduced; this "quiz system" continues for many years.
1870's
1871: Corresponding wing added to the Perry Mansion on the Amity Street side serving chiefly for the "accommodation of additional United States sailors". This increases bed capacity of facility by 70 beds for a total of 200 beds. By this time, over 10,000 "indoor patients" per year are treated in the hospital. Ambulance service is started. Facility’s ambulances are kept in a stable on the north side of Pacific Street, across from the hospital.
1875: Post-mortem examinations are made by students under the direction of instructors. LICH’s annual announcement states: "This plan has been successfully carried on for years in the University of Berlin and is now, we believe, for the first time introduced to this country."
1880's
1880: On May 25, 1880 the Association of Alumni of the Long Island College Hospital is formed and Dr. Alexander J.C. Skene is voted the first president. The Alumni Association experienced rapid growth and activites during its first five years.
1882: A new laboratory for the use of students in chemistry made available and extensive changes made to the main building.
1883: The School of Nursing is established. The residence for the nurses is a house on the southeast corner of Henry and Pacific streets. Irene Sutliffe is the first Superintendent of the Training School and begins to organize both student instruction and overall nursing care in the hospital.
1885: Sanitary Science, an early form of public health, is added to the LICH curriculum in the Department of Physiology.
1888: The Hoagland Laboratory, one of the first major research and teaching facilities for infectious diseases in the US, is completed on the site of the old nurses’ residence on the southeast corner of Henry and Pacific Streets.
Donated by Mr. Cornelius Hoagland, a Regent of LICH, the laboratory was built for research in bacteriology.
Hoagland’s first Director was Dr. George M. Sternberg, the nation’s foremost bacteriologist, already well-known for his studies on disinfection, malaria and yellow fever. Possibly stimulated by the presence of Dr. Sternberg and the Hoagland Laboratory, the clinical departments at LICH become "germ-conscious."
The Arnold Steam cooker is used for sterilizing dressings in Maternity.
1890's
1890: An extra story is built on the Amity Street wing and on a portion of the building between the wing and the original center structure. The Annual Announcement for 1889–1890 states that students are being taught the details of aseptic practice and antiseptic midwifery.
1891: Tuberculin sent to the Hoagland Laboratory by Dr. Robert Koch in Germany. This was one of the first uses of tuberculin in the study of tuberculosis in the US.
1894: The Brooklyn Bureau of Pathology-Bacteriology opens at LICH. Attention is turned to the bacteriology of milk and milk pasteurization and certification (gastrointestinal disease is still the leading cause of morbidity/mortality in young children). Dr. Ezra Wilson, first Director of the Bureau of Pathology, Bacteriology, and Disinfection.
1895 - Diptheria antitoxin prepared at LICH is employed clinically, perhaps for the first time in the US.
1897: Fire destroys the hospital on Ellis Island and an agreement is made between LICH and the US government for the reception and treatment of sick immigrants landing at the Port of New York.
The Collegiate Division begins a four-year graded course of instruction for medical students.
1898: The Polhemus Memorial Clinic Building (begun in 1896) opens and includes a dispensary as well as teaching facilities for medical students. (Henry Ditmas Polhemus)
The War Department asks LICH to care for sick and wounded soldiers of the Spanish-American War. The US Marine and Army Hospitals send patients to LICH for diagnosis with the aid of the new X-Ray machine in Polhemus.
1900's
1902: J. Rogers Maxwell, then President of the Board of Regents, builds a new hospital in memory of his brother Henry W. Maxwell, the preceding President. The central part is built in the courtyard of the old building and completed before any of the old structure is demolished.
1905: The Long Island Society of Anesthetists is founded by A. Frederick Erdmann, a Hospital Anesthetist and Instructor in Anesthesia at Long Island College Hospital. The first meeting was held in the Polhemus Building on October 6 to coincide with Ether Day. This was only the second specialty society in the world and would eventually become the American Society of Anesthesiologists.
1907: The South wing of the old building demolished and the current building started.
Study of milk-souring bacteria Bulgaricus is carried out. Hoagland Laboratory was then in a Middle Eastern neighborhood and researchers had learned about fermented milk-leban (yogurt). Their taste for it leads them to study it bacteriologically.
1910's
1910: Watershed year in the history of medical education in general and at LICH. The Flexner Report, a landmark study rating American medical colleges is published and LICH receives a B rating. (Abraham Flexner, American educator)
Changes suggested in the report carried out over the next four years:
- 8 full-time faculty added.
- Physiology and Pharmacology laboratory courses added with increased lab hours in other courses.
- Work started on Pathological Museum.
- One year of pre-medical college work required for admission.
1914: Inspired by a B rating from the Flexner Report of 1910 the changes made to LICH result in The American Medical Association recognizing the medical school as a Grade A college of medicine.
1915: The North wing of the new Henry Street building, the Arbuckle Memorial, is built through the generosity of Christine Arbuckle and Catherine Arbuckle Jamison in memory of their brothers, Charles and John Arbuckle. This wing increases the capacity of the hospital by 171 beds for a total of 500 beds.
1917: Doctors and nurses from LICH join armed services and several serve in a naval unit composed of personnel from both the Brooklyn and Long Island College Hospital.
Dorothy Bocker, a transfer student would be the first female graduate of The Long Island College Hospital in 1919. She would go on to be Director of the Clinical Research Bureau of the American Birth Control League (ABCL) founded by Margaret Sanger.
1920's
1920: During the 1920's LICH provides care for many crippled children in the epidemics of infantile paralysis.
1923: The Collegiate Division becomes affiliated with the Department of Public Welfare of the City of New York. At this time medical students are sent for clinical instruction to Kings County, Greenpoint, and Kingston Avenue Hospitals.
1929: Dr. Jean Redman Oliver, becomes chairman of the Department of Pathology in 1929. He is the first to conduct the microdissection of individual kidney nephrons to demonstrate their morphology, pathology, and metabolism. He remains chairman until 1954, when he is named the first Distinguished Professor of the State University of New York.
1930's
1930: The Collegiate Department of LICH separates from the Hospital to become The Long Island College of Medicine, an independent institution with its own Board of Trustees. Although the College of Medicine and LICH separate from an administrative standpoint, the activities of the college and its affiliation with the hospital for teaching purposes continue uninterrupted.
1931: A Laboratories Building (subsequently called Polak Laboratories) constructed just east of the Hoagland Laboratory on Pacific Street. It is made possible by a gift from Dr. John Osborn Polak, Class of 1891 and Professor of Obstetrics and Gynecology from 1911 until his death in 1931. Major facilities in physiology, pharmacology, pathology and bacteriology are housed there.
Children with infantile paralysis who require close observation and long treatment are kept in the hospital. The Outpatient Department in Polhemus sees many others who require braces or apparatuses of some sort. To supply these at minimum cost, the hospital maintains its own shop with skilled mechanics.
1932: Viennese psychiatrist Dr. Alfred Adler, who coined the phrase "inferiority complex", joins the staff as visiting professor of medical psychiatry. His theory of individual psychology—that social drives and needs were the key to human behavior—was part of a controversy with Freud that kept the field divided for years.
1940's
1941: LICH along with Brooklyn and Methodist Hospitals, takes steps to increase the number of students graduating because the armed forces are in need of medical officers and a long war is anticipated. The College begins an accelerated schedule of continuous teaching so students will graduate in 3 years instead of 4. LICH along with the Brooklyn Hospital helps to establish the 79th General Hospital, which serve overseas in Ireland, England, and France.
1942: A series of annual postgraduate courses in industrial medicine is given (1942–1948). These courses are designed to promote efficiency and productivity in the war effort. Alexander Garcia (1943) and William P. Riley (1944) were Presidents of the two upper classes, pictured in their uniforms in the lobby of the Polhemus Memorial Building.
1946: Postgraduate refresher courses offered for doctors discharged from the armed forces through an association with the Medical Society of the County of Kings.
1948: The State University of New York, established by the state legislature in 1948, begins a study of medical school facilities with a view to carrying out its mandate of providing an expanded program of medical education and research.
1950's
Fundamental discoveries of the mechanism of cardiac excitation are made by Dr. Chandler McCuskey Brooks, along with Dr. Brian Hoffman and Dr. Mario Vassale. Brooks’ outstanding early work contributed significantly to the development of today's human cardiac pacemakers.
Family planning services first introduced into a New York City municipal hospital (Kings County) and the first gynecological oncology program in the US established by Louis Hellman, MD, Chairman of OB/GYN.
The first hospital-based training program for nurse-midwives and the first Trauma Service Center in the US are established.
1950: The Long Island College of Medicine merges with the newly created State University of New York on April 5, 1950 to form the State University of New York College of Medicine at New York City.
1953: Basic discoveries about DNA repair mechanisms made by Evelyn Witkin, MD. Evelyn M. Witkin receiving the 2002 National Medal of Science from President George W. Bush.
1955: Heart-lung machine development pioneered by Clarence Dennis, MD who uses it in New York State’s first successful open-heart surgery. This machine is now in the collection of the Smithsonian.
1956: The new campus and Basic Sciences Building on Clarkson Avenue opens. The Class of 1957 would be the first graduating class to see the new building in operation.
1960's
1962: Field-dependent/Field-independent research pioneered by Herman Witkin, MD.
1964: SUNY Downstate/Kings County Hemodialysis Program is established as the nation’s first federally funded dialysis unit.
1966: The University Hospital at Downstate (UHD), the College of Nursing, the College of Health-Related Professions and the Graduate School are added. Governor Nelson A. Rockefeller gives dedication address.
1969: The SUNY Downstate Health Sciences University Chapter of The Society of the Sigma Xi, the international research society, was established on April 8, 1969. The national organization granted 47 Charter members and 7 Charter Associate members. Sigma Xi activities continue to this day under the leadership of Dr Subrata Saha.
1970's
1971: Dr. Samuel Kountz came from Stanford University to become professor and chairman of the Department of Surgery. He is credited with having performed more kidney transplant operations than any other surgeon in the United States.
1972: Pathogenesis and pathophysiology of hyperglycemic non-ketotic coma is described by Hugh J. Carroll, MD. Dr. Carroll later describes the pathogenesis of hypoeninemic hypoaldosteronism, discovers techniques of osmometric measurement, describes hyperchloremic acids in the uncontrolled diabetic, develops a method for measuring intestinal absorption of alkali and discovers a new disease in humans called D-Lactic Acidosis.
1973: The world’s first portable hemodialysis machine (Suitcase Kidney) conceived and built by Eli Friedman, MD.
1977: First human images in the world using magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) are produced by Raymond Damadian, MD.
1978: Endothelium-derived relaxing factor (EDRF) is discovered by Robert Furchgott, PhD, who would later be awarded the Nobel Prize for his work on cell surface drug interaction and cardiology research.
1980's
1980: The National Institute of Child Health and Human Development awards a $250,000 grant for the Women’s AIDS Cohort Study, funding one of the first projects to investigate the manifestations of AIDS in women.
Sheldon H. Landesman, MD conducts one of the first studies of HIV infection in women looking at the impact of HIV infection on reproductive choices in women, cervical cancer in HIV infected women and children, pregnancy in HIV infected women, the prevalence of HIV in pregnant women and the development of statistical guidelines for the care of HIV infected women and children.
The Women and Infants Transmission Study is the first to study certain aspects of HIV transmission from mother to fetus. The institution will remain at the forefront in the study of HIV disease in women and children under the direction of Drs. Jack DeHovitz, Howard Minkoff and Hermann Mendez.
1981: Cyclosporine (an anti-rejection drug) is used for the first time in a New York center for kidney transplant patients.
1985: Dr. Gerald Deas and Bill McCreary receive a citation from the Federal Food and Drug Administration's Commissioner Frank E. Young for lobbying the Best Foods Company to post a manufacturer warning label on the ARGO Laundry Starch box. The consumption of the starch as a snack was contributing to iron-deficiency anemia in black woman.
The institution is renamed the State University of New York Health Science Center at Brooklyn (SUNY HSCB).
1987: Ground breaking for a new Health Science Education Building. This building will house the Medical Library of Brookyn, the Colleges of Nursing and Health-Related Professions and study carrels and classrooms for the College of Medicine. Mayor Edward I. Koch, President Donald Scherl, MD, and Governor Mario M. Cuomo at the groundbreaking ceremony.
1989: The Division of Humanities in Medicine established. This interdisciplinary free-standing Division is responsible for the teaching of ethics and other humanities content in the Colleges of Medicine, Nursing, Health-Related Professions and the Graduate School. It will initiate the Strategic Plan for the Archives and establish ethics committees and an active ethics consultation service at UHD, KCHC and LICH.
1990's
1990: During the 1990's, Dr. Henri Begleiter, funded by the largest NIH grant of its kind, detects a brain abnormality in the sons of alcoholics.
1991: The gene responsible for Marfan’s Syndrome discovered by Brendan Lee, PhD and colleagues. The first American-Eastern European academic medical exchange program welcomes Czechoslovak physicians into the center’s PhD program.
An academic Emergency Medicine department is established, the first in a NYC medical school.
1992: Arthur Ashe, tennis great and champion of civil liberties, inaugurates the Arthur Ashe Institute for Urban Health at the Health Science Center on December 3, 1992. It is to be one of his last public appearances.
Patent on critical aspect of a new imaging technique using back-scattered near-infrared light to be used in optical diffusion tomography issued to Drs. Randall Barbour and Jack Lubowsky.
SUNY HSCB and Long Island College Hospital sign an education affiliation agreement naming Long Island College Hospital as the primary teaching affiliate of the College of Medicine.
1995: The College of Medicine holds its first annual White Coat Ceremony on August 17, 1995 during orientation for the Class of 1999. The program is designed to inspire a psychological contract for empathy and professionalism in medicine from the first day of medical training.
1998: Robert F. Furchgott, PhD receives Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine for identifying the fundamental role that nitric oxide (NO) plays in the regulation of cardiovascular function. He is SUNY’s first nobel laureate in any discipline.
2000's
2002: Master’s degree in public health offered through the College of Medicine with the first graduating class in 2002.
2006: Neurology researchers Todd Sacktor, MD, and André Fenton, PhD turn their attention to the issue of how memory is stored.
2008: SUNY officially inaugurates the School of Public Health Initiative. Dr. Pascal J. Imperato becomes the first Dean.