The Ocular Imaging Service
The Ocular Imaging Service aids in the diagnosis of a wide range of ocular disorders by providing physicians with comprehensive, highly detailed images of structures within the eye. Sophisticated ocular images typically are used to formulate a more effective treatment plan. Ocular imaging also is used to detect plateau iris syndrome, or a partially dislocated lens.
At the referring physician's request, University Ophthalmic Consultant's ocular imaging test reports can include a complete evaluation by an UOC consultant, or images can be submitted to the referring physician without interpretation.
Available Tests
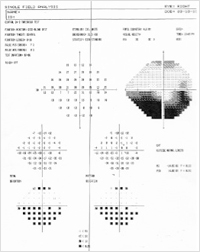
Visual Field Testing – Frequency Doubling Perimetry (FDT) has been shown to be the most sensitive test for detecting the initial defects caused by glaucoma. In addition, both conventional Automated Visual Field testing and blue-on-yellow (SWAP) visual field testing are available. SWAP testing demonstrates visual field loss as many as five years earlier than conventional testing, and it is more sensitive in detecting advancing visual field changes. Screening, full threshold, 24-3, 30-2, and customized testing are available upon request.
Nerve Fiber Layer Measurement – Measurement of nerve fiber layer thickness is performed with the NFA/GDxscanning laser polarimeter, as well as with the Heidelberg Retinal Tomography (HRT). Testing is completed in seconds and may document changes in nerve fiber layer thickness in very early disease, as well as in advanced optic atrophy with extensive cupping or pallor. This test is useful in glaucoma suspects, as well as in patients with documented glaucoma and other causes of optic neuropathy. Pupil dilation is not necessary. The HRT unit provides a measurement of the nerve fiber layer as well as an analysis of optic nerve topography.
Disc Topography – Heidelberg Retinal Tomography computerizes c:d ratio, rim area, and cup area for comparison to a normative database and future self-comparative analysis. This instrument is currently considered the most reliable available for disc analysis. It also measures nerve fiber layer thickness.
Ultrasound Biomicroscopy – Ultrasound Biomicroscopy (UBM) to evaluate the chamber angle without medication in a dark versus light room is the methodology of choice for determining if an angle is physiologically occludable. UBM can also be used to determine if an angle is occludable after iridectomy (in plateau iris syndrome).
UBM has proven increasingly useful for defining anterior segment pathology in patients with complex disease. Ultrasound biomicroscopy is available for imaging pathologic structure and physiologic abnormalities in the anterior segment with a resolution of 50 microns.
Uses include identification and location of intraocular lens haptics, location of glaucoma drainage tubes, vitreous strands, determining the integrity of scleral wounds, and locating inadvertent filtration blebs and cyclodialysis clefts. Using biomicroscopy to evaluate these and many other abnormalities allows the implementation of more exact treatment modalities.
Corneal Pachymetry – Studies have shown that abnormal corneal thickness can lead to a false high or low intraocular pressure reading, as well as independent high risk factor for progressive disease. Using appropriate nomograms, corneal thickness measurements can be used to obtain a closer approximation of the true intraocular pressure.
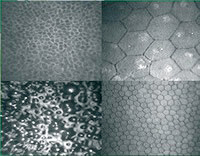
Confocal Microscopy – Exquisitely fine imaging of the corneal layers- allows study of all layers of the cornea under high resolution and high magnification.
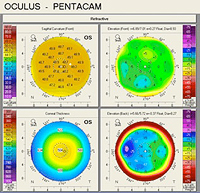
Corneal Topography – Corneal topography with the Pentacam instrument can be highly useful in managing patients with keratoconus and regular and irregular astigmatism, as well as in a host of other corneal conditions.
Specular Biomicroscopy – Specular biomicroscopy is used to evaluate corneal dystrophies and anterior segment dysgenesis. It also is a useful aid in pre-operative evaluation of patients scheduled for cataract and other surgical procedures.
Anterior Segment Photography – This photography permits evaluation of lid position, external conjunctival lesions, and other anterior segment disorders. Gonio-photography is also available.
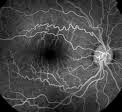
Fluorescein Angiograpy – Digital fluorescein angiography is performed by a certified ophthalmic photographer. It is useful in the diagnosis and management of a host of iris and retinal disorders. Digital angiography allows instant viewing of the images obtained, as well as the ability to transmit the images instantly via modem and the internet.
IOL Master – Extremely precise measurements of eye length and subsequenty, IOL measurements.
Indocyanine Green (ICG) Angiography - ICG angiography is useful in the diagnosis and management of sub-retinal disorders, including choroidal neovascularization, which are poorly imaged with conventional angiography.
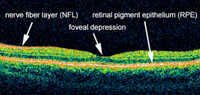
HD Spectral Domain Optical Coherence Topography (HD-OCT) – Precise study of the retinal layers to aid in diagnosis and treatment of a host of different retinal diseases and glaucoma.
To Schedule a Test
Tests should be scheduled through the Flatbush or Brooklyn Heights locations (see contact information below). On the day of the test, referred patients must bring with them a completed request form. Forms are faxed to referring physician offices upon request.
Contact Us
For further information, to make a referral or to schedule an appointment, please call:
University Ophthalmic Consultants at Flatbush
phone: (718) 270-1714
fax: (718) 522-2971
1520 Flatbush Avenue, 2nd Floor
Brooklyn, NY 11210
University Ophthalmic Consultants at Brooklyn Heights
phone: (718) 780-1530
fax: (718) 780-1258
26 Court Street, Suite 1710
Brooklyn, NY 11242