
Peter Bergold, PhD
Professor
Physiology and Pharmacology
Neurology
Dr. Bergold received his PhD in 1986 at Weill-Cornell Medical College in Molecular Biology. He did a post-doctoral fellowship in Neuroscience from 1986-1990with Dr. James Schwartz at the Howard Hughes Institute at Columbia University College of Physicians and Surgeons.
He joined the faculty of SUNY-Downstate Health Sciences University as an Assistant Professor of Physiology and Pharmacology and became a Professor with tenure in 2009. Between 2007-2013, he directed the Graduate Program in Neural and Behavioral Sciences. Dr. Bergold has been recognized as highly effective teacher of both graduate and medical students and was awarded the Chancellor’s Award in Teaching in 2001. He has mentored 16 PhD students and 4 post-doctoral fellows.
In the last 15 years, Dr. Bergold has studied the pathophysiology and treatment of traumatic brain injury. His recent research has focused on the development of chronic neurodegeneration subsequent to a single head injury. His research has generated more than 60 original research manuscripts, invited reviews, and book chapters and has one US patent. This research has been funded by the National Institutes of Health and the Department of Defense. He has also served on multiple grant review committees for the National Institutes of Health and the Department of Defense that focus on traumatic brain injury and post-traumatic stress disorder.
Education
- Undergraduate: Trinity College
- Advanced Degree: Weill-Cornell Medical College
My laboratory is interested in the pathophysiology, diagnosis and treatment of neurodegenerative diseases, in particular, traumatic brain injury (TBI).
TBI now is recognized as a major public health problem, yet there are no treatments for TBI. Two major reasons why drugs have failed clinical trials is that TBI produces a heterogeneous injury and mild TBI is the most common head injury and patients with mild TBI often do not seek medical help for days after injury. An effective drug to treat TBI needs high potency when dosed days after injury. The drug combination, minocycline plus N-acetylcysteine repairs both injury to white matter when first dosed at 12 hours post-injury and limits gray matter injury when first dosed at 72 hours. The drugs modulate inflammation, restores memory and limits neuronal loss. Both drugs have FDA-approval for uses other than TBI suggesting that the combination is both safe as well as effective.
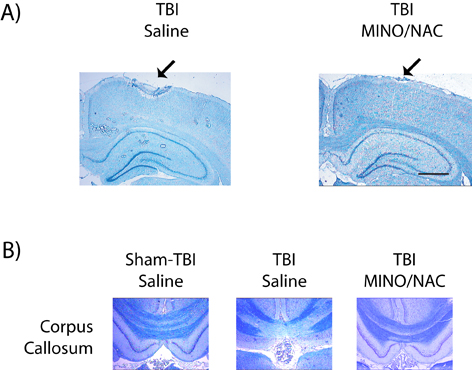
Figure 1. Traumatic brain injury is prevented by minocycline (MINO) and N-acetylcysteine (NAC). A, Representative coronal brain sections. The impact site is indicated with an arrow. The scale bar corresponds to 100 μm. B, Representative images of corpus callosum stained with myelin-specific stain luxol fast blue. Myelin loss in TBI saline-treated brains was partially restored by treatment with MINO plus NAC.
PersonnelElena Nikulina, Ph.D., Postdoctoral Fellow
Kristen Whitney, B.S. Graduate Student
Karrah St. Laurent-Arriot, B.S., Medical Student
Reviewer, Special Emphasis Panel/Scientific Review Group ZGM1 RCB-0 (SC)
Reviewer, Paul G. Allen Frontiers Group- Concussion Proposals
- Abdel Baki, S. G., Kao, H. Y., Kelemen, E., Fenton, A .A., and Bergold, P. J. (2009). A hierarchy of neurobehavioral tasks discriminates between mild and moderate brain injury in rats. Brain Res. 1280, 98-106.
- Abdel Baki, S. G., Schwab, B., Haber, M., Fenton, A. A., and Bergold, P. J. (2010). Minocycline synergizes with N-acetylcysteine and improves cognition and memory following traumatic brain injury in rats. PLoS One 5, e12490.
- Grin'kina, N. M., Abdel-Baki, S. G., and Bergold, P. J. (2013). Reversible behavioral deficits in rats during a cycle of demyelination-remyelination of the fimbria. PLoS One 8, e53775.
- Haber, M., Abdel Baki, S .G., Grin'kina, N. M., Irizarry, R., Ershova, A., Orsi, S., Grill, R. J., Dash, P., and Bergold, P. J. (2013). Minocycline plus N-acetylcysteine synergize to modulate inflammation and prevent cognitive and memory deficits in a rat model of mild traumatic brain injury. Exp. Neurol. 249, 169-177.
- Diaz-Arrastia, R., Kochanek, P. M., Bergold, P., Kenney, K., Marx, C. E., Grimes, C. J., Loh, L. T., Adam, L. T., Oskvig, D., Curley, K. C., and Salzer, W. (2014). Pharmacotherapy of traumatic brain injury: state of the science and the road forward: report of the Department of Defense Neurotrauma Pharmacology Workgroup. J. Neurotrauma 31, 135-158.
- Grin'kina, N. M., Li, Y., Haber, M., Sangobowale, M., Nikulina, E., Le'Pre, C., El Sehamy, A. M., Dugue, R., Ho, J. S., and Bergold, P. J. (2016). Righting reflex predicts long-term histological and behavioral outcomes in a closed head model of traumatic brain injury. PLoS One 11, e0161053.
- Bergold, P. J. (2016). Treatment of traumatic brain injury with anti-inflammatory drugs. Exp. Neurol. 275 Pt 3, 367-380.
- Tsokas, P., Hsieh, C., Yao, Y., Lesburgueres, E., Wallace, E. J., Tcherepanov, A., Jothianandan, D., Hartley, B. R., Pan, L., Rivard, B., Sajan, M. P., Bergold, P. J., Hernandez, A. I., Cottrell, J. E., Shouval, H. Z., Fenton, A. A., and Sacktor, T. C. (2016). Compensation for PKMzeta in long-term potentiation and spatial long-term memory in mutant mice. eLife 5.
- Womack, K. B., Paliotta, C., Strain, J. F., Ho, J. S., Skolnick, Y., Lytton, W. W., Turtzo, L. C., McColl, R., Diaz-Arrastia, R., and Bergold, P. J. (2017). Measurement of peripheral vision reaction time identifies white matter disruption in patients with mild traumatic brain injury. J. Neurotrauma 34, 1539-1545.
- Haber, M., Jessica, J., Kim, J., Sangobowale, M., Irizarry, R., Ho, J. S., Nikulina, E., Grin'kina, N., Hartman, I., Ramadani, A., and Bergold, P. J. (2017). Minocycline plus N-acetylcysteine induce remyelination, and synergistically protect oligodendrocytes and modify neuroinflammation in a rat model of mild traumatic brain injury. J. Cereb. Blood Flow and Metab., in press.